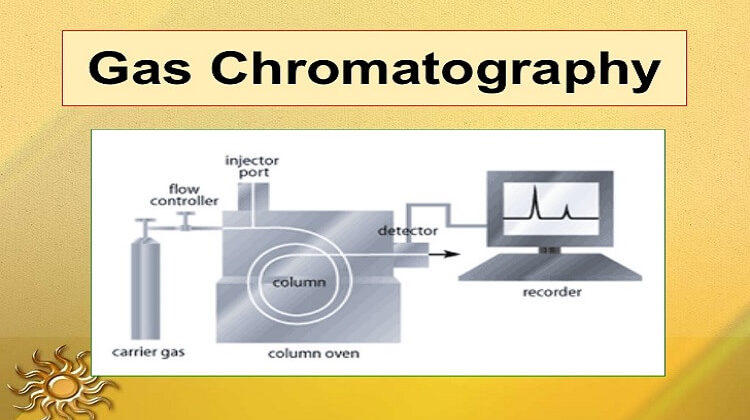
Gas chromatography is very different from other forms of chromatography. It uses gas, and its components are separated as vapours. That is why it can detect and isolate small molecules’ compound weight in the gas phase. Furthermore, the sample used in this phase is liquid or gas that is then vaporized in the injection port.
Gas Chromatography
The stage for gas chromatography is helium because of its lightweight and is chemically inert. Then pressure is applied, and the mobile phase moves and analytes through the column. This separation is accomplished by a column that is coated in the stationary phase.
How Does It Work?
The mobile phase and the stationary phase are two phases between which the samples are divided. The equilibrium creates a partitioning for the samples. Compounds with a higher affinity in the stationary phase spend more time in the column and have higher retention time than those with lower affinity.
Therefore, intermolecular interactions often drive relationships in the stationary phase, and that is why the stationary phase can be used to maximize interactions. The separation is accomplished by partitioning the gas and a thin layer of non-volatile liquid held on reliable support. A sample containing solutes is injected in a heated block where it evaporates immediately.
Furthermore, they are absorbed in the stationary phase and then absorbed by a new gas carrier. This process is repeated in each plate sample as it moves towards the outlet. Each solute travels at its own pace through the column. These bands will separate into zones depending on the partition coefficients and band spreading.
The solutes then enter into the detector attached to the exit end of the column. The appearance weight, time, height, and area of these peaks can be measured to get quantitative and qualitative data.
Benefits of Gas Chromatography
Gas Chromatography is a beneficial and popular mode of the channel to detect specific chemical properties. Many industries and companies use this method to understand the differences in the molecules of different gas. You can also use liquids and solids in gas chromatography after converting them into gas. Moreover, it is extensively used in forensics sciences.
Components of Gas Chromatography
The main components of gas chromatography are:
- Gas carrier in a high-pressure cylinder with attendant pressure regulators and meters.
- Sample injection system
- Separation column
- Liquid phases
- Nonpolar
- Intermediate polarity
- Polar
- Hydrogen bonding
- Specific purpose phases
- Supports
- Detector
- Recorder
Procedure
Step 1: Sample Injection and Vaporization
- Draw a small amount of liquid sample in a syringe.
- Insert the syringe in the hot injection port quickly.
- Since the sample enters the gas chromatograph simultaneously, it is crucial to insert it quickly.
- The temperature is high to vaporize the sample quickly.
- The vaporized components are then mixed to be carried to gas chromatography to be separated.
Step 2: Separation in Column
- The component that absorbs most strongly in the stationary phase will spend the most time in this column.
- The component that absorbed least strongly will spend the least time in this column.
- Then results are detected through two different samples, one that absorbs most and the other absorbs least.
Step 3: Recording Results
- Components reach the end at different times because of the differences in the time spent in the column.
- The retained component in the shortest time will reach first, and the part that spends most time will reach the end.
- The detector then sends signals to record the results.
Advantages
- The higher velocity and longer columns allow the gas to separate in a few minutes.
- It is very reliable in industrial applications.
- Versatile technique since high temperatures allows the possibility to convert any material into the volatile component.
- Favoured for nonpolar molecules
- It is usually used in applications where small molecules are detected and with non-aqueous solutions.
Disadvantages
- The component that you will analyze needs to be under certain gas chromatograph conditions.
- Compounds analyzed are small since it is challenging to analyze larger components.
- The vapour pressure should be greater than zero.
- The samples should be salt-free without ions.
- The substance is minimal in amount, and thus it is needed to be checked through a sample containing a pure suspected substance to analyze.
Conclusion | Gas Chromatography
Gas chromatography is very accurate if it is used properly. The analysis is used to calculate the content of a chemical product. Gas chromatography is used to analyze oils such as oil spills, essential oils during perfume separation, air-borne pollutants, and drugs used to enhance athletes’ performance is measured through a urine test.

